Lesson 1: Alkanes
Today, we'll dive into some key functional groups: alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, haloalkanes, and arenes, along with interesting real-world examples to illustrate their importance.
Welcome to Masters of the Universe!
Hello, budding chemists! As you embark on your journey into the fascinating world of organic chemistry, one of the first and most crucial concepts you’ll encounter is functional groups. Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that determine the chemical properties and reactions of those molecules. Today, we'll dive into some key functional groups: alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, haloalkanes, and arenes, along with interesting real-world examples to illustrate their importance.
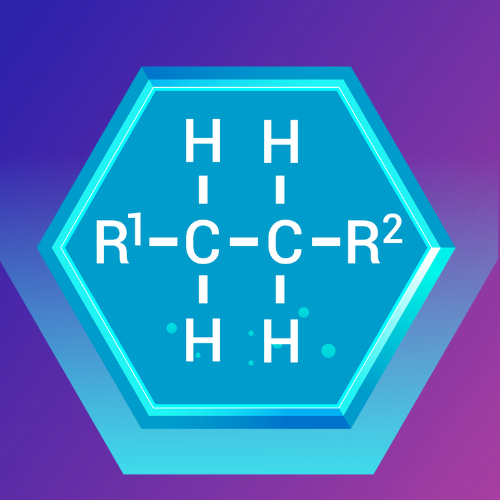
Alkanes: The Simple Hydrocarbons
What Are Alkanes?
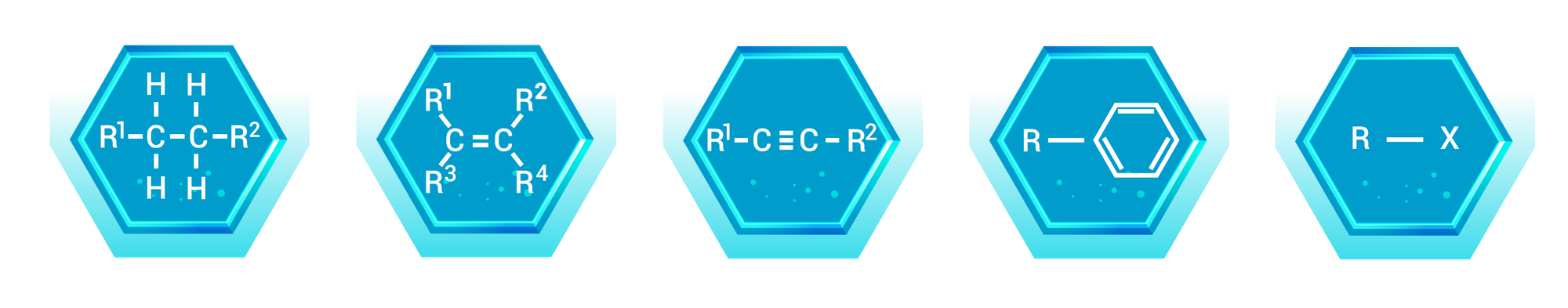
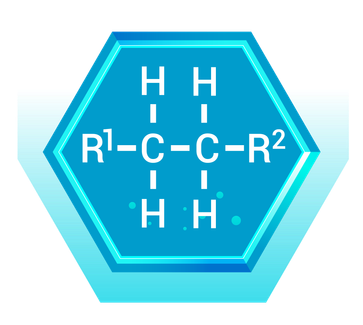
Alkanes are the simplest type of hydrocarbon, consisting only of carbon and hydrogen atoms connected by single bonds. They are also known as saturated hydrocarbons.
Real-World Example: Methane (CH₄)
- Description: Methane is the simplest alkane, consisting of one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms.
- Application: Methane is a major component of natural gas, which is used as a fuel for heating, cooking, and electricity generation. It's also a significant greenhouse gas, playing a role in climate change.
Alkenes: The Double-Bonded Hydrocarbons
What Are Alkenes?
Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. This double bond gives alkenes distinct chemical properties compared to alkanes.
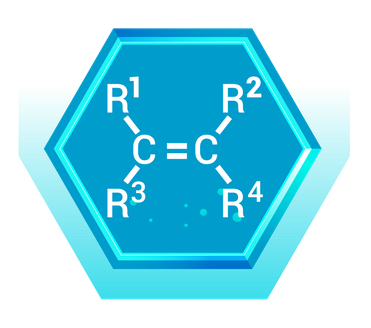
Real-World Example: Ethylene (C₂H₄)
- Description: Ethylene is the simplest alkene, with two carbon atoms connected by a double bond and each carbon also bonded to two hydrogen atoms.
- Application: Ethylene is widely used in the production of polyethylene, a common plastic found in packaging materials, containers, and household products. It's also a plant hormone that regulates fruit ripening.
Alkynes: The Triple-Bonded Hydrocarbons
What Are Alkynes?
Alkynes are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. This triple bond makes alkynes more reactive than alkanes and alkenes.
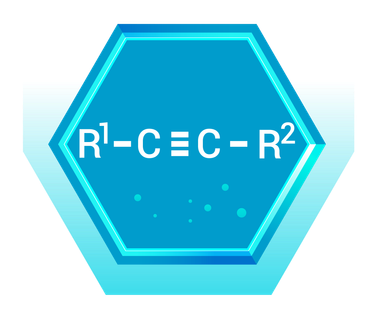
Real-World Example: Acetylene (C₂H₂)
- Description: Acetylene is the simplest alkyne, with two carbon atoms connected by a triple bond and each carbon also bonded to one hydrogen atom.
- Application: Acetylene is used as a fuel in welding and cutting metals. The high-temperature flame produced when acetylene burns in oxygen is ideal for these applications.
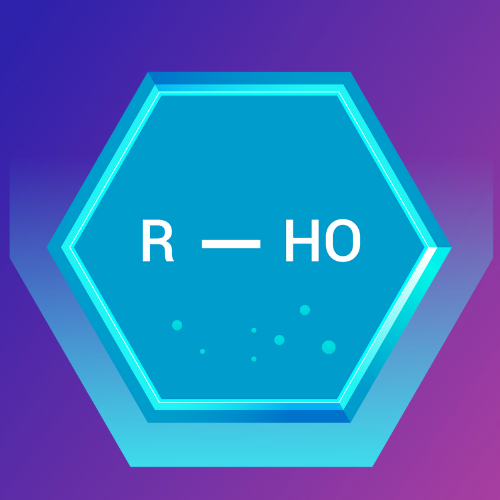
Haloalkanes: The Halogen-Substituted Hydrocarbons
What Are Haloalkanes?
Haloalkanes, also known as alkyl halides, are hydrocarbons in which one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by halogen atoms (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine) typically represented by an X.

Real-World Example: Chloroform (CHCl₃)
- Description: Chloroform is a haloalkane with one carbon atom bonded to three chlorine atoms and one hydrogen atom.
- Application: Historically, chloroform was used as an anesthetic. Today, it is primarily used in the production of the refrigerant R-22 and as a solvent in laboratories.
Arenes: The Aromatic Hydrocarbons
What Are Arenes?
Arenes, also known as aromatic hydrocarbons, are compounds that contain at least one aromatic ring—a stable ring of carbon atoms with alternating double bonds.
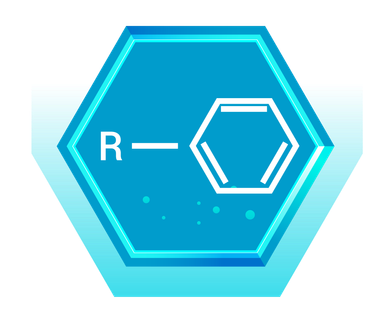
Real-World Example: Benzene (C₆H₆)
- Description: Benzene is the simplest arene, consisting of a six-carbon ring with alternating double bonds and each carbon bonded to one hydrogen atom.
- Application: Benzene is a fundamental building block in the chemical industry, used to manufacture a variety of chemicals, including plastics, resins, and synthetic fibers. However, it is also a known carcinogen, and its use is heavily regulated.
Ready to Play Level 1 in ChemEra: To Alpha Centauri?
Understanding functional groups is essential for mastering organic chemistry. Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, haloalkanes, and arenes each play significant roles in both the chemical industry and everyday life. By recognizing these functional groups and their real-world applications, you’ll gain a deeper appreciation for the diverse and dynamic nature of organic chemistry. Now try our minigame ChemEra when you subscribe for free.
Stay curious and keep exploring the wonders of chemistry with Masters of the Universe!
Why ChemEra: To Alpha Centauri is helpful for Learning
- Interactive Learning: By combining gameplay with educational content, ChemEra: To Alpha Centauri turns the memorization of chemistry concepts into an interactive and enjoyable experience.
- Engagement: The game’s space adventure theme keeps players engaged and motivated, making it easier to retain information about chemical structures.
- Skill Reinforcement: Each level reinforces your knowledge of chemistry, ensuring you become proficient in recognizing and recalling their names and structures.
- Accessibility: Designed to be played on mobile devices, this game makes learning convenient and fun, anytime and anywhere.