Lesson 3: Acyl Halides, Esters, Ethers, Epoxides, and Amines
In this post, we’ll dive into acyl halides, esters, ethers, epoxides, and amines. Along with the definitions, I’ll provide interesting real-world examples to illustrate their importance.
Welcome to Masters of the Universe!
Hello, future chemists! Today, we’re continuing our journey into the fascinating world of functional groups. Understanding these groups is crucial for mastering organic chemistry. In this post, we’ll dive into acyl halides, esters, ethers, epoxides, and amines. Along with the definitions, I’ll provide interesting real-world examples to illustrate their importance.

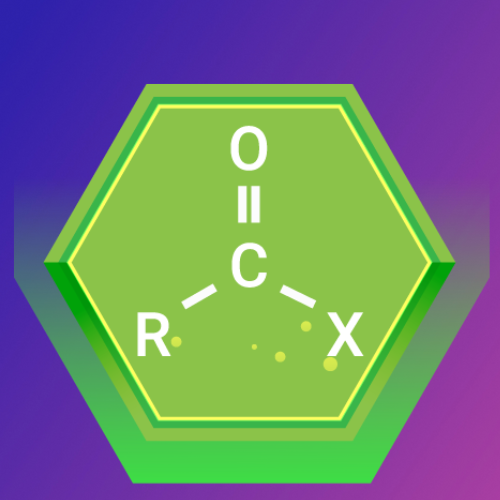
Acyl Halides: The Reactive Carbonyl Compounds
What Are Acyl Halides?
Acyl halides (also known as acid halides) are organic compounds derived from carboxylic acids by replacing the hydroxyl group (-OH) with a halide (X). They are highly reactive due to the presence of the carbonyl group (C=O) adjacent to a halide.

Real-World Example: Acetyl Chloride (CH₃COCl)
- Description: Acetyl chloride is a simple acyl halide with a two-carbon chain where one carbon is part of the carbonyl group bonded to a chlorine atom.
- Application: Acetyl chloride is widely used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and dyes. It is also employed in acylation reactions to introduce acetyl groups into compounds.
Esters: The Pleasantly Scented Compounds
What Are Esters?
Esters are organic compounds formed by the reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. They contain the functional group -COO- where a carbonyl group (C=O) is bonded to an oxygen atom that is also bonded to another carbon atom.

Real-World Example: Ethyl Acetate (CH₃COOCH₂CH₃)
- Description: Ethyl acetate is a common ester with a four-carbon chain where two carbons form the ester group.
- Application: Ethyl acetate is used as a solvent in paints, coatings, and adhesives. It is also found in perfumes and flavorings due to its pleasant fruity smell.
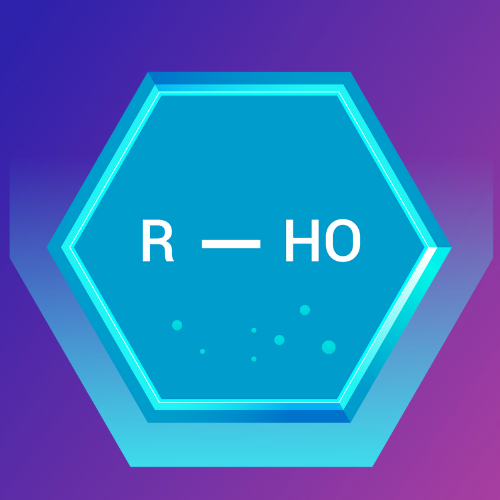
Ethers: The Simple Oxygen Linkers
What Are Ethers?
Ethers are organic compounds characterized by an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. The general formula for an ether is R-O-R', where R and R' are the alkyl or aryl groups.

Real-World Example: Diethyl Ether (C₂H₅OC₂H₅)
- Description: Diethyl ether, commonly known as ether, consists of two ethyl groups bonded to an oxygen atom.
- Application: Diethyl ether is used as a solvent and was historically used as a general anesthetic. It is also employed in the manufacture of other chemicals.
Epoxides: The Reactive Three-Membered Rings
What Are Epoxides?
Epoxides are cyclic ethers with a three-membered ring structure containing an oxygen atom. This strained ring makes epoxides highly reactive.

Real-World Example: Ethylene Oxide (C₂H₄O)
- Description: Ethylene oxide is the simplest epoxide, consisting of a three-membered ring with two carbon atoms and one oxygen atom.
- Application: Ethylene oxide is used for sterilizing medical equipment and as a precursor in the production of ethylene glycol (antifreeze). It is also employed in the synthesis of various chemicals.
Amines: The Nitrogen-Based Compounds
What Are Amines?
Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia (NH₃) by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms with alkyl or aryl groups. They can be primary, secondary, or tertiary, depending on the number of alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom.

Real-World Example: Aniline (C₆H₅NH₂)
- Description: Aniline is a primary amine with a phenyl group attached to an amino group.
- Application: Aniline is used in the manufacture of dyes, pharmaceuticals, and rubber processing chemicals. It is also a precursor to many industrial chemicals.
Ready to Play Level 3 in ChemEra: To Alpha Centauri?
Understanding functional groups is essential for mastering organic chemistry. Acyl halides, esters, ethers, epoxides, and amines each play significant roles in both the chemical industry and everyday life. By recognizing these functional groups and their real-world applications, you’ll gain a deeper appreciation for the diverse and dynamic nature of organic chemistry. Now try our minigame ChemEra when you subscribe for free.
Stay curious and keep exploring the wonders of chemistry with Masters of the Universe!
Why ChemEra: To Alpha Centauri is helpful for Learning
- Interactive Learning: By combining gameplay with educational content, ChemEra: To Alpha Centauri turns the memorization of chemistry concepts into an interactive and enjoyable experience.
- Engagement: The game’s space adventure theme keeps players engaged and motivated, making it easier to retain information about chemical structures.
- Skill Reinforcement: Each level reinforces your knowledge of chemistry, ensuring you become proficient in recognizing and recalling their names and structures.
- Accessibility: Designed to be played on mobile devices, this game makes learning convenient and fun, anytime and anywhere.